The posterolateral corner (PLC) of the knee is a complex network of ligaments and soft tissue structures that stabilise the outer (lateral) aspect of the knee. Its three main components are the lateral collateral ligament (LCL), the popliteus tendon, and the popliteofibular ligament. Working together, these structures provide critical stability — particularly against forces that push the knee inwards or cause it to rotate outward.
PLC injuries typically occur from high-energy trauma, such as motor vehicle or motorbike accidents, or from a direct blow to the inside of the knee that forces it into hyperextension and rotation. They can also occur in athletes — especially in contact and pivoting sports such as AFL, soccer, rugby, and skiing — often in combination with other ligament injuries.
These injuries often cause significant swelling and pain along the outside of the knee, making it difficult to bear weight. As pain settles, the knee may feel unstable or “give way,” particularly during side-to-side movements.
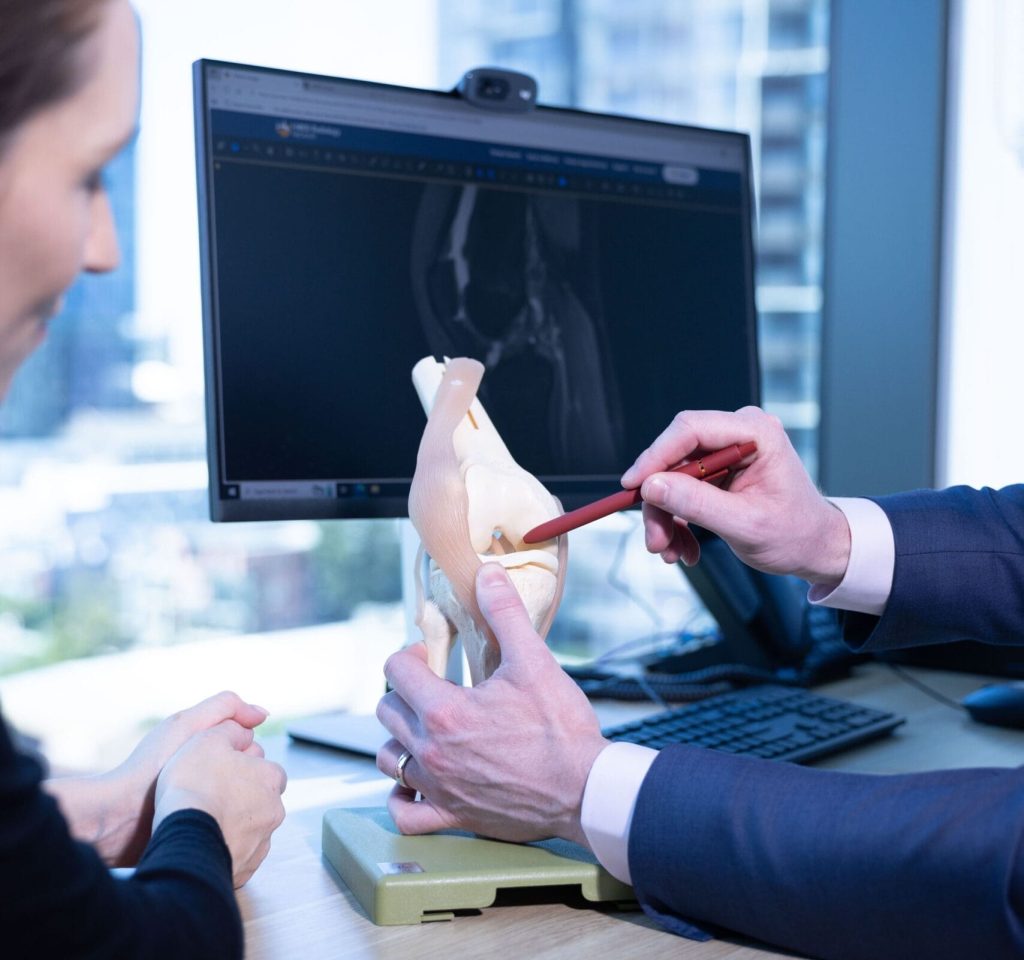
An experienced clinician can often suspect a PLC injury based on the history and physical examination. X-rays help exclude associated fractures, while an MRI scan is the gold standard for confirming the diagnosis and identifying any related ligament or cartilage damage.
PLC injuries are complex and frequently occur alongside other ligament injuries. Mild sprains without significant instability may be managed without surgery, using bracing, crutches, and physiotherapy. However, high-grade injuries with marked laxity usually require surgical reconstruction to restore stability and protect other knee structures from further damage.
Dr Free has extensive experience in diagnosing and treating complex posterolateral corner injuries. He uses advanced, evidence-based surgical techniques tailored to each patient, aiming to restore knee stability, optimise function, and protect long-term joint health.
Dr Matthew Free offers expert, personalised solutions for every step of the journey.